
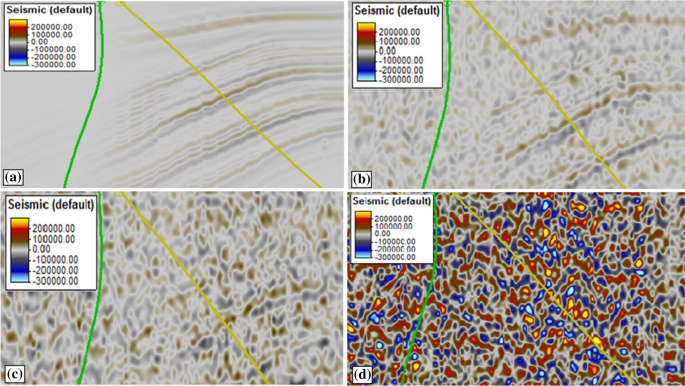
Finally, we analyze the Teapot stacked and depth-migrated subsets to show random and coherent noise removal, leading to an improvement of the volume structural details and overall lateral continuity. Convergence velocity calculated according to. Then, we use the Penobscot subset to illustrate random noise and footprint signature attenuation, as well as to show how faults and fractures are improved. Circles with a colour scale show the hypocentre location of the upper plate earthquakes 7, aftershocks of the M w 8.1 Iquique earthquake were filtered. We use the Waipuku subset to indicate the signal preservation of the method in good-quality data when mostly background random noise is present. We determine the performance of SSOF using three public domain field data sets, which are subsets of the well-known Waipuku, Penobscot, and Teapot surveys. In contrast to other SOF techniques, such as anisotropic diffusion, anisotropic smoothing, and plane-wave prediction, SSOF does not require any iterative process to reach the denoised result. It is able to process a 3D data volume with a 2D strategy using basic 1D edge-preserving filters. SSOF relies on a few parameters that are easily tuned and on simple 1D convolutions for tensor calculation and smoothing. this dissertation is focused on quantitatively investigating the. The new method can suppress stronger erratic noise compared with the previous iterative method, and can better deal with random noise compared with the singlestep implementation of the median filter. Orders for current subscriptions and back issues should be sent to EAGE Publications BV, Journal Subscriptions, PO DB, Houten, The Netherlands. Simple seismic viewer with mapping capabilities and trace filtering. Flagship Joint Impedance and Facies Inversion to estimate facies and elastic properties directly from post/pre-stack seismic data. These self-adaptive paths are given by the eigenvectors of the smoothed structure tensor, which are easily computed using closed-form expressions. The median filter is applied following the slope direction of the seismic data to maximally preserve the energy of useful signals. Key features include: seismic dip estimation, structure oriented filtering, multi-trace 3D/4D post/pre-stack time shift estimation, frequency slice filtering and dip steered AVO gradient stabilization. The method, called spectral SOF (SSOF), allows us to enhance the signal structures in the f- x- y domain by running a 1D edge-preserving filter along curvilinear self-adaptive trajectories that connect points of similar characteristics. Of the Mines JTK.We have developed an algorithm to perform structure-oriented filtering (SOF) in 3D seismic data by learning the data structure in the frequency domain.
STRUCTURE ORIENTED FILTER SEISMIC ROKDOC SOFTWARE
The software that implements this conjugate gradient method for solving the anisotropicĭiffsuion equation can be found within the solve method in the LocalSmoothingFilter class The top of headslope width shall be transitioned at 30:1 or flatter back to the top of approach fill width away from the Transportation Structure.
STRUCTURE ORIENTED FILTER SEISMIC ROKDOC PLUS
, describes an implementation of this algorithm by implicitly solvingĪ modified version of the diffusion equation via conjugate gradient iterations. If head slopes are used at the end of a Transportation Structure, the top of headslope widths shall be the out-to-out Structure end width plus at least 2 m. Input parameters in the anisotropic diffusion process. This diffusion is guided along the structure present in the image by computed structure tensors that serve as

Image as an initial condition, we simulate the anistropic diffusion process which diffuses the seismic amplitudes of the input image By solving the anisotropic diffusion equation using the input seismic The gist of these filters is a smoothing operation parallel to the seismic reflections that does not operate beyond reflection terminations (faults).

The underlying algorithm that performs this adaptive smoothing is known as anisotropic diffusion filtering and has been usedĮxtensively in image processing applications. We discuss a class of filters that removes noise and, if desired, simplifies structural information in 3D seismic data.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
